The question “What do you think of hormone replacement therapy?” is one of the most common I get asked as a health practitioner focused on women’s health. Read on to learn more about HRT and other options.
Are You Dangerously Low in Magnesium?
Root Causes of Hashimoto's with Dr. Eric Osansky
Dr. Eric Osansky is a chiropractic physician, clinical nutritionist, and Functional medicine practitioner. He is back on the show in the event of his new book coming out called "Hashimoto's Triggers". In this episode we talk about Hashimoto's disease & its triggers, the connection between thyroid & SIBO, and essential oils.
Here's what you'll hear:
Min 01:05 Introducing Dr. Eric Osansky's new book
Min 02:55 What are Hashimoto's triggers?
Min 04:25 Food triggers
Min 08:00 Estrogen dominance
Min 12:10 The connection between thyroid & SIBO
Min 18:10 Blood sugar as a trigger for Hashimoto's
Min 21:55 Blue light exposure
Min 23:45 Dr. Osansky's book
Min 24:05 Using essential oils
To learn more about Dr. Osansky, visit his website here and follow him on social media:
Facebook
Resources:
Hashimoto's Triggers book
Addressing Hashimoto's and Graves' Disease with Dr. Eric Osansky
Receive a FREE CHAPTER from Dr. Osansky's book "Hashimoto's Triggers"
Here's a video version of the interview with Dr. Eric Osansky:
Ready to Support Your Thyroid?
Check out my free guide on simple hacks for thyroid support!
You want help for your thyroid symptoms ASAP! Cut to the chase with this straight-forward guide, outlining the exact techniques I use to help keep my Hashimoto’s in remission.
Let me help you start addressing your symptoms now!
What to Do About Heavy Periods
Are you avoiding social events because of your heavy period? Missing work? Soaking through a great outfit, or your mattress? How about getting on birth control for your wedding to avoid a blood bath on your special day?
If you have heavy periods, they can be very inconvenient. They can also be exhausting.
I always say that your period blood isn’t ‘extra blood’, it’s real substance that your body made with work and nutrients. And it’s work to make it all over again. Now, if you health is good and your flow is normal, it’s all good. But when your flow is excessive, you can end up depleted.
This article will help define what a heavy period is, why it happens, and some great ideas on what to do about it. So let’s get started!
1. How Much is Too Much Menstrual Bleeding?
The range of normal flow is 10-60 ml, according to the National Health Service of the UK.
According the Centre for Menstrual Cycle and Ovulation Research, the average flow a woman has is 30 ml, or 2 Tablespoons. It doesn’t sound like much, but it’s 6 soaked tampons or pads. Considering that most women will have a heavy day or two, and a few light days (4-6 days in total), this sounds about right.
Over 60 ml or over 80 ml (depending who you ask), i.e. 16 soaked menstrual pads, is considered menorrhagia- very heavy menstrual bleeding often with clots and flooding. Women in last category will often experience iron-deficient anemia (inadequate red blood cell count).
While it’s normal to have a heavy day or two, if you have to always pair a tampon with a pad, or re-arrange your schedule around your flow, it’s too much. If you have heavy multiple heavy days, like 4+ heavy days, it’s also too much. If you find yourself very exhausted and short of breath due to your period, these are further symptoms.
2. What Causes Excess Menstrual Bleeding?
The most common reason for heavy bleeding is estrogen dominance. First let’s define estrogen, and how it affects your cycle.
Estrogen is a hormone that influences many processes in your body, from bone formation to clear thinking. Estrogen is mainly made in the ovaries, although it can also be made by the adrenal glands or in your fat tissue.
Each time you have a period, your hormone levels drop. When they drop, the brain registers this change and signals your ovaries to make more estrogen. This estrogen ripens a new egg for the next period cycle, and the estrogen grows your uterine lining.
This growth phase is fairly short. You have your period for 4-6 days (ideally), and then your build the lining up for about another ten days. At day 14 (ideally), you ovulate. While you continue to make estrogen, another hormone, progesterone, becomes the dominant player after ovulation. The progesterone firms up and matures your uterine lining, making it hospitable for a potential pregnancy.
Now let’s say this ideal picture is disturbed by too much estrogen, or not enough progesterone to balance out the estrogen. Then you get more growth in you uterine lining. This means more blood at period time, and can lead to big clots too.
There are lots of reasons for estrogen dominance. Not all of them will apply to you (: So I’m giving a clear heading for each type, so you can scan over them and see which may be a match for you. In section three, we’ll cover ways to address these issues, so keep reading!
A. You Are Getting Your First Periods
When you have your first period as a young woman, estrogen levels pump up! As your ovaries come to life, your brain and ovaries learn how to dance together, and your first few years of cycling can be irregular. Heavy, painful periods are commonly reported in teenage women.
This does not mean you have to just accept your fate or get on birth control pills. Many young women have a poor diet and are being exposed to chemicals and growth hormones. Please see the ‘What Can You Do About Heavy Bleeding?’ section for tips!
B. You are Overweight
Your fat cells house an enzyme called aromatase, used in the manufacture of estrogen. The higher your percentage of body fat, the more estrogen you can produce. As you reduce stored body fat, your estrogen production will lessen as well. Ironically, when you lose weight you will release estrogen that was stored in that fat tissue, and you can become more hormonally imbalanced in the process. So lose weight at a moderate pace.
As you age, the lowered amount of estrogen you produce can slow your metabolism and lead to more weight gain, especially in the middle. Conversely, the amount of estrogen you produce in your fat and other peripheral locations can cause an estrogen overload and heavy periods. Sometimes it’s just not fair! (Source)
C. You are Exposing Yourself to Chemicals and Food Additives
Before I became educated, I would look at my shampoo bottle and its list of chemical ingredients and think, “well I’m sure these are safe for me or they wouldn’t be in here.” Nope.
According to a 2013 article in the NY Times, “In its history, the E.P.A. has mandated safety testing for only a small percentage of the 85,000 industrial chemicals available for use today. And once chemicals are in use, the burden on the E.P.A. is so high that it has succeeded in banning or restricting only five substances, and often only in specific applications: polychlorinated biphenyls, dioxin, hexavalent chromium, asbestos and chlorofluorocarbons.”
Many of these chemicals are xenoestrogens, or chemical compounds that look like estrogen to the body. When these chemicals get inside of you, through eating them, rubbing them on your skin, or inhaling them, they attach to estrogen receptors in the body. That means your cells get the estrogen message, and to the uterine lining that means “grow”!
That’s why it’s so important to limit your exposure to these compounds, at any age. For a some women, these compounds could mean heavy periods. For other women, they can contribute to breast and other cancers. (Source)
D. You Have an Underactive Thyroid
Thyroid disease is skyrocketing in our culture. According to the American Thyroid Association, more than 12 percent of the U.S. population will develop a thyroid condition during their lifetime and women are five to eight times more likely than men to have thyroid problems.
Your low thyroid activity can lead to low reproductive hormone production. This can mean you don’t ovulate as often, or that you make less progesterone.
When you have low thyroid activity you also have decreased sex hormone binding globulin (SHBG), which can mean that more estrogen in circulation, leading to heavy periods. (Source)
To complicate matters, high estrogen can bind up thyroid hormone, feeding the imbalance!
E. You Are Not Ovulating
Here’s some news that most women don’t seem to know; just because you have periods doesn’t necessarily mean you are ovulating. Sometimes the body seems to be cycling, because it is trying to achieve that, but it’s kind of going through the motions.
This can be due to stress, due to being underweight or nutrient deficient, due to perimenopause, or due to polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS). Whatever the cause, if you don’t ovulate, then you’re going to make less progesterone (which is made after ovulation), so you won’t have that to balance out the estrogen production.
If you don’t ovulate you can also get your period in a very delayed timeline, so then the estrogen is left unchecked for even longer.
F. You Have Low Progesterone
This cause is a cousin to the ‘you are not ovulating’ cause above. Even if you do ovulate, if you ovulate a poor quality egg, or have other hormone production problems, then the estrogen is left somewhat unchecked. This may also cause spotting and breakthrough bleeding in weeks 3-4 of your cycle.
G. You Are in Perimenopause
During perimenopause (the ~ 10 years before menopause), you ovarian function starts to decline. The eggs are generally not as good of quality anymore, though some are better than others. Estrogen is being made well some months, and not so well other months. So some months you’ll have a more normal cycle, and other months you can flow quite early, late or heavily.
To some extent this is ‘normal’, as the body is aging and getting ready to leave its reproductive phase. (It’s sad; I know.) But there are ways to ease the transition too.
H. You Have Fibroids or Endometriosis
Fibroids are masses that form in or on your uterus. Estrogen dominance is generally to blame for how these grow in the first place. Then to make matters worse, they respond to the cyclic hormonal changes of your menstrual cycle, and grow and shed like your uterine lining.
This can cause very heavy bleeding and can lead to anemia.
Some women can have a separate condition called endometriosis. Uterine tissue migrates outside the uterus, for example, around the abdomen. When a woman menstruates, endometrial tissue - wherever it is in the body - bleeds.
I. You Have Recently Given Birth or Had a Miscarriage
Birth
After I gave birth to my son, I was shocked by how much bleeding I had for so long. Though everyone generously gave me blankets and baby toys, no one warned me about this!
According to the folks at What To Expect, “the heaviest of the bleeding will last for about three to ten days after labor and delivery and then it should taper off to lighter spotting after pregnancy. You'll see the difference in the color as this starts to happen, from red to pink, then brown, and finally to a yellowish white. Lochia (mix of blood, mucous, tissue) should stop flowing around four to six weeks after delivery.”
I definitely remember bleeding for a least a month. If you continue the bleed heavily after 10 days (like changing a pad every hour), contact your doctor. Even if you had a C-Section, you will still be expelling blood and loch after birth.
Miscarriage
I have never had a miscarriage, but I’ve heard some horror stories from my clients.
If you are less than eight weeks pregnant when the miscarriage occurs, the expelled tissue will look no different from heavy menstrual bleeding. The further along you are in pregnancy, the heavier the bleeding and more severe the cramps.
According to Maricopa OBGYN page,
“During the miscarriage, you may bleed heavily, soaking a pad every 10 minutes. The cramping can be quite uncomfortable.
Although cramping, bleeding and occasional clotting is normal after both a miscarriage and a D&C, you should not be soaking more than 2 pads an hour nor experience worsening, exquisite pain after the uterus has been emptied. These are important symptoms to report to you doctor.
During your recovery, you will continue to bleed, on and off, for up to 3 weeks. Some minor cramping will continue in the next few days also. If bleeding increases or stays bright red, or if you have foul-smelling discharge or a fever or persistent cramping, contact your health care provider.”
J. Uterine and Cervical Cancer
It is possible that heavy bleeding could arise from uterine or cervical cancer. These conditions could involve heavy flow or spotting at random times, or after sex. The odds are that your heavy flow or spotting is due to an item in above list.
Cervical cancer usually will not process to heavy bleeding unless the disease is quite progressed. The best prevention is to practice safe safe and to get a pap smear every 5 years or as directed by your physician. Cervical cancer often develops from certain strains of the Human Papillomavirus (HPV).
Uterine cancer is more comely diagnosed in women over 50 years old, although there are other risk factors such as obesity and a history of irregular cycles. Every year, about 52,000 U.S. women are diagnosed with uterine cancer, according to the National Cancer Institute.
K. Hemophilia
It is possible that you will have heavy bleeding due to a blood clotting disorder. If you are missing clotting factors VIII or IX, you will also experience easy bruising or nose bleeds, and can have very heavy bleeding after childbirth. You will probably have menstrual pain as well. This condition is rare, 1 in 5,000 - 10,000 for type A and 1 in 50,000 - 100,000 in type B, but if you suspect this, especially if there is heavy bleeding in your family, ask your doctor.
3. What Can You Do About Heavy Bleeding?
As I shared above, the most common reason for heavy bleeding is estrogen dominance, so let’s start there for solutions:
A. Avoid Xenoestrogens
Xenoestrogens are synthetic chemicals that look and act like estrogen in your body. When these are present, it’s easy to get into estrogen dominance and heavy periods. The top tips are:
Eat organic
Use all natural cleaning and beauty products
Avoid using plastics for cooking and food storage.
B. Watch your Weight
Estrogens are also made in your fat tissue through a process called aromatization. If you are trying to eat right and exercise but can’t lose weight, avoid xeno-estrogens, check your thyroid, make sure you get a good night’s sleep.
C. Check Your Thyroid
I love Izabella Wentz’s ‘safety theory’ that theorizes that when your body is under stress (emotional, chemical, or pathogenic), it dials down thyroid production as a way to get you to safely hibernate. It’s fascinating. Read about it here.
If you do get your thyroid checked, be sure to do it up right, getting a full thyroid panel and having it interpreted by a functional medicine type practitioner. Jen Wittman of Thyroid Loving Care has some great info on that here.
D. Try Herbs and Supplements
I am not a fan of using supplements unless you have a solid base of good habits, and have checked for other underlying causes. But I will mention a few nice supplements here, and you can check with you doctor if it’s safe for you to use them.
1. Vitex - This herb, that is also called chaste tree berry, seems to benefit communication between your ovaries and your brain, and it’s especially good at increasing progesterone. It may not be as useful for women in their late 40s, and it may not be a fit for everyone, but it has many success stories. It can be taken daily throughout your cycle. Use for 6 months, unless you have an adverse reaction.
2. Di-Indoly Methane (DIM)- DIM is a star at clearing excess estrogen. It’s often used for PCOS (polycystic ovarian syndrome) but it can be useful in most any case of estrogen dominance. For more information, see this blog at NaturoDoc. According to Dr. Holly Lucille, ND, RN, DIM shifts estrogen metabolism to the healthy 2-hydroxy pathway (makes for nice skin) in place of the troublesome 16-hydroxy pathway (makes for heavy periods and cancers).
3. Calcium-D-Glucarate (CDG)-This is one I’ve just learned about recently. CDG also does a great job at clearing spent estrogen from the body. Here’s some cool information on how it works from Dave Asprey at bulletproof.com:
“One of the ways the body gets rid of toxins is through a process called conjugation. During conjugation, toxins are packaged into water soluble compounds called glucuronides. Glucuronides are meant to pass from the liver, to the bile, then to the gut where they are excreted. However, high levels of an enzyme called beta-glucuronide can inhibit this process. This enzyme separates toxins from their conjugate bond and allows them to be reabsorbed. This allows toxins to keep circulating in the body where they make you fat, tired, and weak.
Calcium-d-glucarate prevents beta-glucuronide from disturbing this process. It keeps the toxins bound inside a glucuronide which is then removed from the body. Toxins are most damaging in their free form, which is why you want them to be bound (conjugated) and released from the body. Calcium-d-glucarate inhibits beta-glucuronidase which allows toxins to be removed.”
E. Heal Your Gut
You might be surprised to hear that your digestive tract has anything to do with heavy periods! But it’s so. Your gut is the place where food is broken down into the nutrients you need to make hormones. It’s also the place where used hormones are broken down and expelled. So it needs to be a healthy environment, free of inflammation, full of good bacteria, and moving daily.
This is a big topic to cover, but here are two top tips:
Chew your food and eat a relaxed fashion. Gulping down food while scanning your smartphone does not lead to proper digestion.
Eat a variety of fibers daily/ weekly. Fibers from berries, nuts, seeds and vegetables will fuel the friendly bacteria in your gut. And don’t get stuck eating the same 4-5 things; mix it up for greater bacteria diversity.
F. Try Chinese Medicine
Chinese medicine can be a relaxing way to balance your hormones. Herbal formulas like Bu Zhong Yi Qi Tang, and treatments like moxibustion on your spleen 1 point can stop a heavy flow. Look for a practitioner who specializes in women’s health in your area. If you’re in Portland, Oregon, come check us out at Blue Sky Wellness Studio.
G. Zen Out
A major hormone disruptor is stress. It blocks hormone receptors, raises blood sugar and blocks production of reproductive hormones. The reproductive hormone that goes down first is usually progesterone, and you’ve learned you need that to balance out the estrogen.
My best advice here is to focus on having fun. If you stay connected with friends, go to a delicious meal with your sweetie, or take a work break to visit the sauna (I did this today), it’s hard to stay obsessed with your problems. Problems will always be there, so seize the moment and enjoy life!
H. Seed Cycling
Seed cycling means taking certain nuts and seeds in the first 2 weeks or your cycle, and another type in the second two weeks. The alternating phases support first your estrogen production and then your progesterone production, plus the fiber helps clear spent hormones. I already wrote a whole blog on this topic, which you can access here.
Wow, thanks for sticking with me and reading this very long article on heavy periods! I hope it helps you. If you’d like more in-depth support, we offer private health coaching here.
Bridgit Danner, LAc, FDNP
Founder of Women’s Wellness Collaborative
Is Low Progesterone Behind Every Hormone Problem?
This article is suitable for: Perfect Periods, Fertility, Post-Partum and Perimenopause
Wondering what the heck is happening with your hormones?!?
I am creating a new online quiz, and as I compiled the reasons behind various conditions- PMS, infertility, postpartum depression, disruptive menopause- one reason was dominating the answer field: low progesterone.
I don’t know why the sheer dominance of the pattern just hit me now after years of research! Hopefully I can save YOU a few more years of hormonal confusion with this article. This article is suitable for women in any stage of life!
What is Progesterone?
Progesterone is a hormone made primarily in the ovaries by the corpus luteum (the tissue left behind after you release an egg at ovulation). It is also made by the adrenal glands, and if you are peri-menopausal or menopausal with infrequent or no ovulation, then you really rely on the adrenals as a source of progesterone.
Progesterone has various functions in the body:
After your ovulate, it helps ‘ripen’ your uterine lining, preparing for a possible pregnancy
Raises your basal body temperature in the second half of the cycle
Serves a precursor hormone to cortisol, your energy/stress hormone made by the adrenal glands
Lifts you mood and calms your body
Benefits sleep
Prevents water retention
Helps the cells utilize fats
Helps maintain blood sugar levels
You can surmise by the list above that if you are low in progesterone, you may have some of the opposite effects- bloated, moody, can’t sleep, craving sugar, gaining weight, and periods are irregular or heavy.
How Does Low Progesterone Happen?
Low progesterone can occur for many reasons that are very common in modern life, which is likely why I am seeing this pattern so frequently with my clients.
1. Estrogen Dominance
Estrogen dominance is both a cause and a result of low progesterone.
It’s a cause because you can get too high in estrogen due to carrying excess body weight, and your fat tissue produces estrogen. Even if you are thin, you can put yourself into excess estrogen if you have high blood sugar and insulin resistance. Insulin resistance is a state in which your cells block insulin from getting inside because your blood sugar is too frequently too high.
Symptoms of blood sugar dys-regulation include: feeling hungry all the time, getting very irritable if you miss a meal (or a snack), fatigue, weight gain around the middle, acne.
The most common hormonal disorder amongst women of reproductive age is PCOS, or polycystic ovarian syndrome. In this condition, there is insulin resistance, high androgen production, and disordered function of the ovaries. This often leads to missing or infrequent ovulation. As you learned already, most of our progesterone is made after you ovulate, so you don't ovulate, then you won't make much progesterone, and you'll be in estrogen dominance.
Another major disruptor are xenoestrogens, which are synthetic compounds that activate estrogen receptors in the body.
Some key sources of xenoestrogens are:
Commercially-raised meat and dairy products
Medications, including birth control pills
Non-organic foods (with traces of pesticide)
Soft plastics
Shampoos, body lotions and perfumes (contain xenoestogenic compounds unless all natural)
Tap water
Food additives
Bleached tampons and sanitary pads
You can see that it’s easy to get exposed to a lot of xenoestrogens in day! The xenoestrogens in your body confuse the feedback loop between your brain and your ovaries. If your liver is overloaded, you won’t break down these xenoestrogens well, and they can get stored up in fat tissue (hello, belly fat) for you body to handle later.
Here’s an article by the Environmental Working Group if you’d like to deepen your research on this topic.
Even if you don't have excess estrogen, if progesterone is low, you can still end up in estrogen dominance.
Estrogen and progesterone play a seesaw game over the course of a month, and over the course of your life as a woman. Estrogen is needed to stimulate your ovaries and grow your uterine lining in the first part of your cycle. This strong first half leads to strong progesterone in the second half, unless something goes wrong. The following points can all be causes of low progesterone.
2. Poor Nutrition
With the busyness of modern life, it’s easy to choose processed foods, caffeinated drinks and sugary pick-me-ups. Living in a grind, without time to reflect and connect, can also draw us towards ‘comfort food,’ or that after-work glass of wine.
Besides these easy-to-make poor choices of modern life, even organic food is not as nutritious as it used to be, due to decreased soil quality. And let’s face it, we don’t alway eat organic, whether it’s because we don't have access, we can’t afford it or we’re eating out.
The last point I’ll mention here is weak digestion. When we’re stressed, have taken antibiotics, don’t chew our food, etc., we aren’t getting the most out of the food we eat.
How does this contribute to low progesterone? We need certain ingredients to make and utilize hormones. You need enough B6 and cholesterol for progesterone production, but there is more to it than that. All our micronutrients (vitamins and minerals) and macronutrients (protein, fat and carbohydrates) are needed for the proper functioning of our coordinated hormonal system.
3. Stress
You are a highly productive woman, but you are likely under chronic stress. (If not, congratulations!) Stress can come from so many places: your commute, the chemicals in your environment, a tense relationship, an undiagnosed dental infection, etc. Chronic stress makes your adrenal glands react with a high level of cortisol…at least at first. In this stage you may feel wired, not be able to sleep, not be able to focus on sex, feel anxious, etc.
As you learned earlier, progesterone is a precursor to cortisol. So if you are making lots of cortisol, is it fair to assume that your progesterone level is being affected? Yup.
Image courtsey of Functional Diagnostic Nutrition (TM)
Have a look at the chart to the right. Not only will you burn through progesterone to make cortisol, your body will start to favor that pathway at the expense of your other sex hormones: testosterone and estrogen (pictured at lower right).
Remember how you learned earlier that progesterone is made mainly by the corpus luteum? There is another hormone that is needed to get you to a nice, strong ovulation: estrogen. Estrogen is made by the ovaries, upon signaling by your brain, to stimulate your ovarian follicles and mature a healthy egg in the first half of your menstrual cycle.
This is why we can’t overly focus on the low progesterone aspect. We have to look ‘upstream’ at what other hormones are being affected and what’s really behind our imbalances.
Low cortisol can be related to some other symptoms like catching colds and flus frequently, getting dizzy easily, or feeling overwhelmed easily.
4. Perimenopause
Perimenopause is the ten year period before menopause during which your ovarian function is declining. For some women, they are still getting a period pretty regularly and feeling pretty good. For others, this ten year period can be tumultuous. After learning about stress and nutrition above, I’m sure you could guess these things could play in to a rockier perimenopause.
But this declining ovarian function is natural. As your egg quality declines with age (even if you’re enjoying low stress and good nutrition) you could still fail to ovulate, or ovulate a ‘weak’ egg, and its corpus luteum may not produce as much progesterone.
As you learned earlier, the adrenals can pick up some slack…as long as they aren’t depleted from years of stress and malnutrition!
There is another change that is occurring too, especially as you get close to menopause: the main type of estrogen you use is changing form estradiol to estrone, and this a big switch for your body. You have different receptors for estradiol versus for estrone, so there can be some ‘wobbles,’ such as memory lapses or hot flashes as you go through this process. You can also have what feels like constant PMS, and that’s no good! Be sure to read our ‘what to do to support progesterone’ section at the end of this article.
5. Postpartum
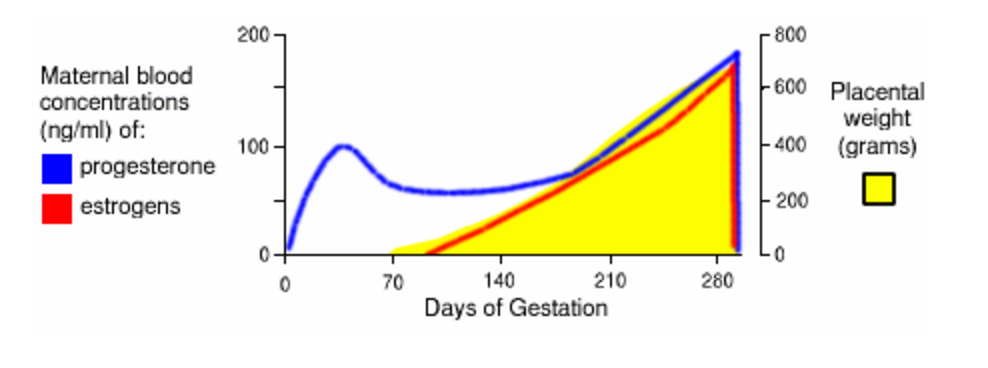
What’s another time that you are not ovulating for natural reasons? Pregnancy and postpartum! While you are pregnant you are on a hormonal high, with corpus luteum and then the placenta producing producing very high amounts of estrogen and progesterone, up to 30-50 times higher than your non-pregnant level!
But after childbirth, your hormones levels drop like a bad habit. This can produce some of the same reactions as in perimenopause, like night sweats and depression.
As you breastfeed, you are high in the hormone prolactin, and that inhibits ovulation. As you are learning no ovulation leads to low progesterone. Again, your adrenal glands can pick up the slack, but if you came into pregnancy with moodiness and poor stress-handling, you likely will end up there again after childbirth. Be sure to read through for our 'fixes' at the end!
6. Low Thyroid Function
Lastly, let’s learn about low thyroid function. If you have an under-functioning thyroid, whether due to Hashimoto’s thyroiditis or another reason, it can affect your progesterone. This happens in two ways:
When you have low thyroid function, you have decreased sex-hormone binding globulin (that’s a mouthful) which binds up sex hormones like estrogen, possibly letting estrogen levels get too high compared to progesterone.
Because thyroid hormone stimulates activity in every area of the body, when thyroid hormone is low, your production of sex hormones will be low.
It’s estimated that up to 15% of Americans have thyroid disease, if you include subclinical hyptothyroidism. Up to 10% of women will experience post-partum thyroiditis. Women are 5-10% more likely to have thyroid disease than men, and the age group over 50 is most at risk. (Source: Your Healthy Pregnancy with Thyroid Disease by Dana Trentini and Mary Shomon,.
How are we getting to this heightened incidence of hypothyroidism? Again, the factors of modern life are the perfect storm for it: high stress, toxins everywhere, an ‘altered’ food supply.
Autoimmune Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis is the leading cause of hypothyroidism. The gut, as we discussed in the Poor Nutrition section and will discuss again in the closing section, is a key area of focus in healing Hashimoto’s. When peptides (parts of the protein in foods) cross the gut barrier into the blood stream it stresses the system and the immune system responds by going after those peptides that shouldn’t be there. But the trouble is that this dysregulated immune system will also attack the body’s own tissue, in this case the thyroid gland.
The most touted symptoms of low thyroid are foggy thinking, cold limbs, fatigue, hair loss, constipation and weight gain. But I fight with hypothyroidism and I am skinny and tend more towards loose stool, and luckily still have all my hair! There are many manifestations of hypothyroidism, so it’s worth taking a deeper look if you suspect you may have hypothyroidism. A great place to start looking is the website of Dr. Izabella Wentz, aka the Thyroid Pharmacist.
What to Do to Support Progesterone Production:
Herbs and Supplements:
Maca- Maca is an adaptogenic herb, meaning it can adapt to find and serve the needs of your body. It can increase your energy by supporting your adrenal glands. My friend Dr. Anna Cabeca, who developed a green drink mix called Mighty Maca, says that in a before and after lab test, her client’s DHEA doubled using Might Maca. DHEA is a precursor to our sex hormones estrogen and testosterone, so that’s great news! Testosterone, by the way, is the dominant sex hormone in men, but women do need and want it for sex drive, muscle tone and confidence, among other things.
Vitamin C- The ‘simple’ vitamin C is greatly needed by your adrenal glands. So boosting your supply of this vitamin helps your adrenal glands make more hormones. Food sources include fresh broccoli (not so much week old broccoli), peppers and lemons. As a supplement, look for alma powder or a vitamin C with bioflavonoids. It’s also in the Might Maca powder mentioned above. You can take quite a bit; I’d suggest 1,000 - 3,000 mg/day. Check with your doctor if you have any special medical conditions.
Vitex- Vitex, or Chaste Tree Berry, has a special ability to support your brain’s communication with your ovaries. This can really support a strong ovulation and a resulting high progesterone level in the second part of your cycle.
Foods:
Avoid processed foods, gluten, dairy, sugar, caffeine and alcohol. According to Dr. Tom O’Bryan, author of the Autoimmune Fix, gluten, sugar and dairy are the three biggest triggers of autoimmunity and inflammation. Learn more in my podcast interview of Dr. Tom.
Fill your day with thing like hot lemon water and smoothies in the morning (I like to pair my smoothie with bacon or sausage), generous salad with nuts and beans at lunch, and fish or meat and veggies in a fat-rich sauce at dinner.
If you have low cortisol, you probably also have low blood sugar and will need a couple healthy snacks between meals. Avoid ‘grazing,’ and don’t snack if you don’t need to, but if you tend to crash dramatically without food, then eat more often.
Remember that you don’t have to avoid natural fats to be skinny, you just have to avoid processed carbs!
Healing:
As we learned earlier a leaky gut (increased intestinal permeability), can increase your odds of autoimmune diseases. It can also decrease your odds of get nutrition out of your foods. So your digestive system is important to heal and maintain. Do this by eating a wide variety of plant fibers- aim for twenty different types a week- to feed your friendly gut flora.
If your digestion is weak, cooked food with just a side of raw salad is best for you. Eat in a calm environment and chew your food well. I recommend a high-quality probiotic, and it may require a higher dose while you heal. You can check out the probiotic we love, MegaSpore Biotic, at our Programs and Products page.
You’ll also need to rest (you read that right). Remember earlier how we said that running around without time to rest and reflect can lead to poor food choices? Beyond poor food choices, it can lead to poor life choices! So take some time each day to let your mind unwind. You can read a book, journal, meditate, nap…whatever you like. It’s great to occasionally take a retreat in a natural setting too. Make sure to get a good night’s sleep each night, as critical healing and rebuilding happens nightly.
For cycling women, we offer a Perfect Periods self-study course to help you identify and treat your root causes of low progesterone! Check it out here.
If you’re not yet subscribed to our newsletter, we’d love to have you! You can do so here, and you’ll receive our Hidden Hormone Stressors Quiz, our video “Is My Cycle Normal?’ and our Ten Ways to Destress ebook.
Lastly, feel free to share this article or leave a comment below. Thanks!
Bridgit Danner, LAc, FDNP